Term
|
Definition
|
| V |
Roman Numeral for 5 |
| variable |
subject to change. A letter or a symbol used to represent a number. For example in the expression 2x + 3 = 9, x is the variable |
| varies |
if x varies directly with y, then x α y and so x = ky, where k is the constant of variation |
| varies inversely |
if x varies inversely with y then x α 1/y and so x = k/y, where k is the constant of variation |
| vector |
object with both magnitude (size) and direction |
| velocity |
speed. The rate of change of distance over time. V = dx/dt |
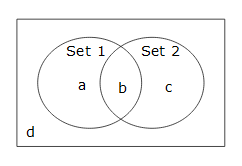
| Venn diagrams |
the name given to diagram to represent two or more sets, most commonly used in probability
 |
| vertex |
corner of a shape |
| vertex of a parabola |
x coordinate = –b/2a |
| vertical |
a line that is straight up and down, perpendicular to horizontal
 |
| vertical line test |
if a vertical line is drawn through a graph and it cuts the graph at only one point, the graph is said to be a function. If it cuts more than once, it is not a function.
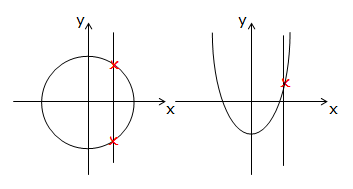 In the first diagram the red line cuts the curve in two places, therefore it is not a function. In the second diagram it only cuts it once, therefore it is a function. In the first diagram the red line cuts the curve in two places, therefore it is not a function. In the second diagram it only cuts it once, therefore it is a function. |
| vertically opposite |
vertically opposite angles are equal to each other
 |
| vinculum |
the line in a fraction separating the numerator (top) from the denominator (bottom) |
| volume |
the amount of space a 3d shape takes up. Formulas for volume vary from shape to shape, the most basic being for a rectangular prism where V = lbh |
| vulgar fraction |
another term for common fraction, any fraction with a numerator (top) and a denominator (bottom) |

 In the first diagram the red line cuts the curve in two places, therefore it is not a function. In the second diagram it only cuts it once, therefore it is a function.
In the first diagram the red line cuts the curve in two places, therefore it is not a function. In the second diagram it only cuts it once, therefore it is a function.